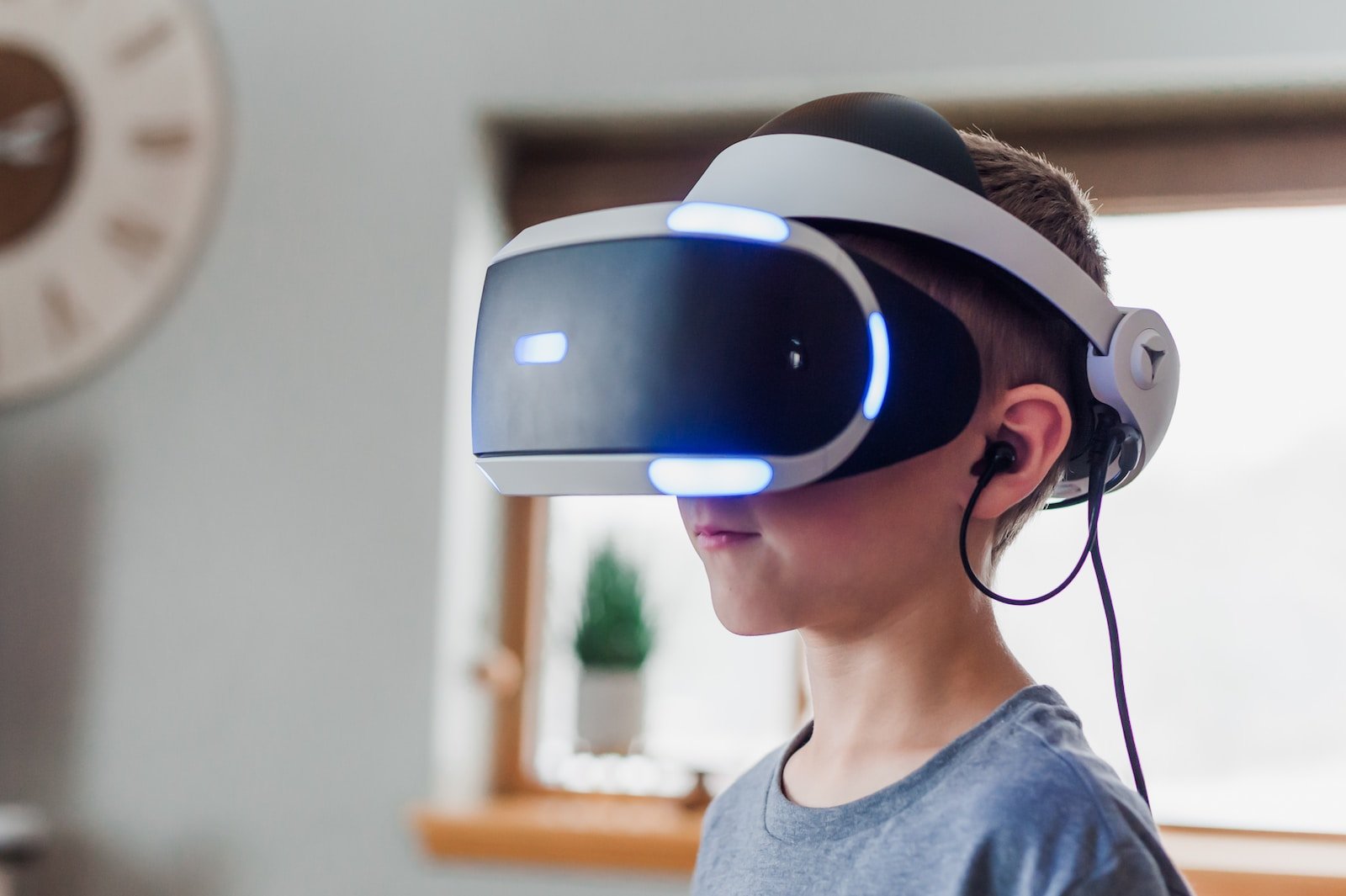
In recent years, the technological landscape has witnessed the emergence of virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and extended reality (XR). Despite the backing of industry giants like Sony, Apple, Meta (formerly Facebook), Samsung, and Microsoft, these immersive technologies are yet to attain the widespread popularity enjoyed by smartphones, smartwatches, or televisions. While poised for growth, VR, along with its siblings AR and XR, faces significant challenges on the path to capturing the hearts of the general public.
1. The Quest for Simplicity: Onboarding Users to VR (H2)
1.1. The Unwritten Rule: Keep it Simple (H3)
In the consumer technology realm, simplicity is often the linchpin for adoption. The unwritten rule is clear: keep it simple, make it easy to understand. However, VR, in its current state, often falls short of this principle. Unlike the seamless activation of a mobile phone or a television, VR devices demand a significant investment of time for setup, ranging from hardware installation to software configuration and user account setup. The onboarding process for VR can be a 15 to 30-minute affair, posing a potential deterrent to widespread adoption.
1.2. Streamlining Onboarding: A Crucial Shift (H3)
The challenge lies in streamlining the onboarding process to make VR more approachable. For VR to become as commonplace as a phone or a smart speaker, manufacturers must prioritize user comfort and minimize the time and effort required for initial setup. This shift towards simplicity is crucial for enticing users from all walks of life.
2. Content Conundrum: Crafting Engaging Experiences (H2)
2.1. The Challenge of Tailored Content (H3)
One of the hurdles that VR faces is the need for specific and compelling content. Unlike traditional platforms such as smartphones or televisions, VR demands content creators to tailor their work for an immersive environment. This implies an additional workload for video game developers, filmmakers, and series creators who wish to tap into the potential of VR. The financial and creative investments required pose risks in an industry already grappling with escalating costs.
2.2. Fostering User-Generated Content (H3)
To address this challenge, the industry can explore avenues to involve users in content creation. Platforms can encourage the creation of 360º content through user-generated contributions, similar to the wealth of content available on platforms like YouTube. Empowering users to contribute to the VR ecosystem can diversify content and potentially mitigate the challenge of exclusive, platform-specific content.
3. Battling Time Constraints and Fatigue (H2)
3.1. The User Experience Dilemma (H3)
The user experience in VR is hindered by a notable challenge—time constraints and physical fatigue. Unlike traditional electronic devices where users can spend hours without issue, VR headsets currently induce physical and visual fatigue after approximately one hour of use. This limitation in usage time presents a stark contrast to the immersive experiences offered by smartphones, televisions, and gaming consoles.
3.2. Prolonged Use without Discomfort (H3)
For VR to win the hearts of the masses, addressing the issue of user fatigue is imperative. The success of devices like Apple’s Vision Pro hinges on their ability to enable prolonged usage without causing discomfort or eye irritation. A VR headset must facilitate extended periods of immersion seamlessly, whether for entertainment, education, or professional applications.
4. The Price of Progress: Accessibility and Affordability (H2)
4.1. Breaking Down Financial Barriers (H3)
While VR devices are becoming more affordable, the financial aspect remains a crucial factor in mainstream adoption. The costs associated with high-quality VR hardware, coupled with the need for powerful computing systems, can create barriers for a significant portion of potential users.
4.2. Democratizing Access to VR (H3)
Addressing this challenge requires a concerted effort to democratize access to VR. Manufacturers and developers need to focus on creating cost-effective solutions without compromising on quality. Initiatives such as VR subscriptions, bundled services, and more accessible hardware options can contribute to making VR a feasible choice for a broader audience.
5. The Role of Education and Familiarity (H2)
5.1. Bridging the Knowledge Gap (H3)
VR’s relative novelty and the lack of widespread familiarity contribute to its challenges. Many potential users remain unaware of the possibilities and benefits offered by VR technology. Educating the public about the potential applications, from education to entertainment, is pivotal in overcoming this hurdle.
5.2. Integration in Educational Curricula (H3)
An effective strategy involves integrating VR experiences into educational curricula. By exposing students to VR from an early age, familiarity with the technology grows, and the apprehension associated with its use diminishes. Collaborations between VR developers and educational institutions can play a crucial role in this integration.
6. The Connectivity Conundrum: The Need for Seamless Integration (H2)
6.1. Seamless Integration in Everyday Life (H3)
For VR to become a seamless part of everyday life, there is a need for enhanced connectivity. VR devices must seamlessly integrate with other smart devices, creating a holistic digital ecosystem. This integration extends beyond hardware compatibility to software interfaces that enable effortless communication between VR and existing technologies.
6.2. Interoperability Standards (H3)
Industry-wide efforts to establish interoperability standards can further facilitate the seamless integration of VR into the digital landscape. This involves collaboration between tech companies to define common protocols that allow different devices to communicate effectively. The absence of such standards can create silos, limiting the fluid interaction between VR and other technologies.
7. Privacy and Ethical Concerns (H2)
7.1. Safeguarding User Privacy (H3)
The immersive nature of VR raises concerns about user privacy. As users delve into virtual environments, the collection and utilization of personal data become potential points of contention. Addressing these concerns requires robust privacy policies, transparent data practices, and user-friendly controls that empower individuals to manage their privacy within VR experiences.
7.2. Ethical Design Principles (H3)
Furthermore, adopting ethical design principles is essential to ensure that VR experiences prioritize user well-being. This involves considerations such as minimizing the risk of addiction, providing adequate breaks during extended use, and avoiding content that may induce discomfort or distress.
8. The Educational Imperative: Building VR Literacy (H2)
8.1. Promoting VR Literacy (H3)
Overcoming the challenges of VR adoption necessitates a concerted effort to build VR literacy among users. This involves not only educating users on how to use VR devices but also fostering an understanding of the potential applications and implications of VR across various domains.
8.2. Collaborative Initiatives (H3)
Collaborative initiatives involving technology companies, educational institutions, and advocacy groups can play a pivotal role in promoting VR literacy. Workshops, online resources, and community engagement programs can contribute to demystifying VR and empowering users to navigate the technology confidently.
Conclusion: Navigating the Future of Virtual Reality (H2)
In conclusion, the journey toward mainstream adoption of virtual reality is marked by multifaceted challenges, each demanding innovative solutions and collaborative efforts. From simplifying onboarding processes to fostering user-generated content, addressing fatigue issues, and ensuring affordability and accessibility, the path ahead requires a strategic and holistic approach.
The industry’s commitment to overcoming these challenges is evident in ongoing advancements, with manufacturers continuously refining hardware, software, and user experiences. As VR evolves, the focus on education, privacy, and ethical considerations becomes paramount. The potential of virtual reality to transform how we learn, entertain, and connect is immense, but realizing this potential requires a collective endeavor to unlock the future of immersive technologies.
As we navigate the evolving landscape of VR, it is not just about creating cutting-edge devices; it is about building a future where virtual reality seamlessly integrates into our lives, enriching experiences and expanding possibilities. With each challenge addressed, we move closer to a reality where virtual becomes an integral part of our everyday existence.