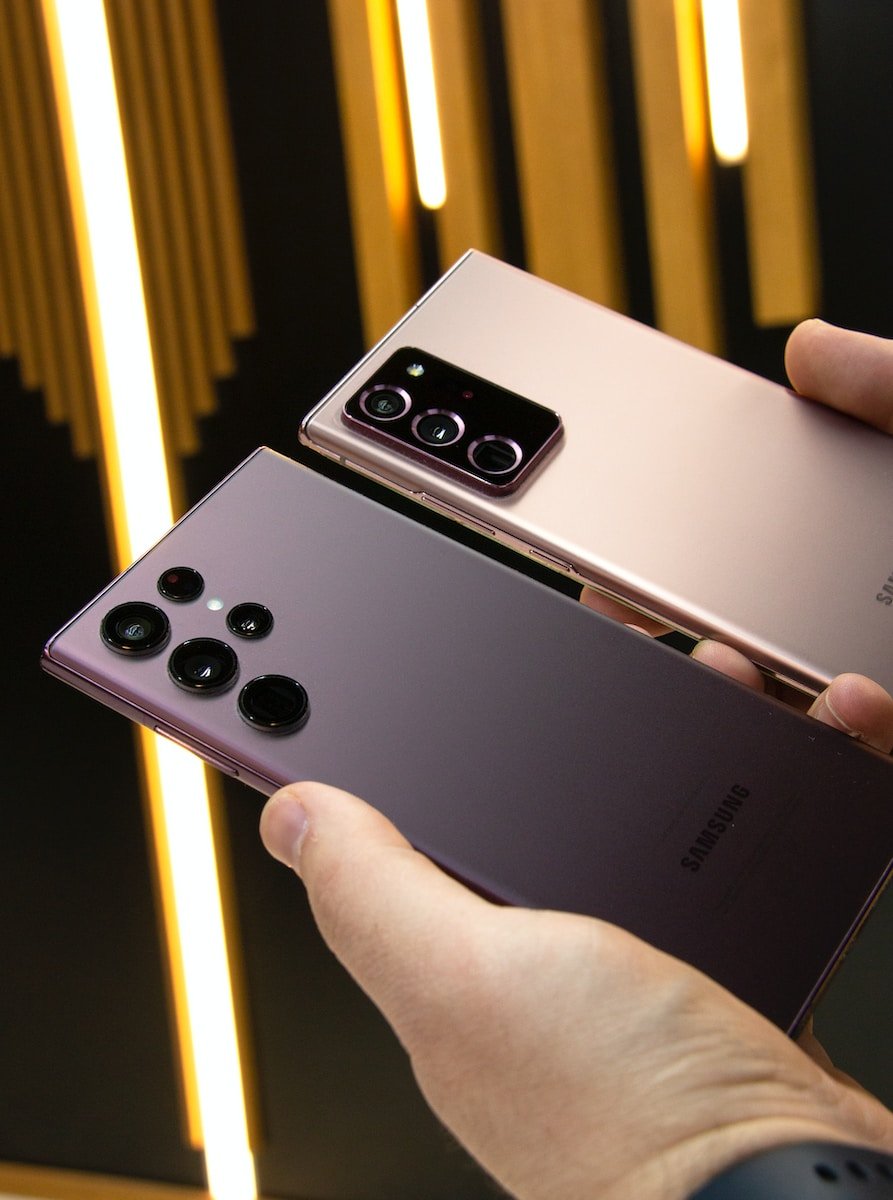
If you’ve ever perused smartphone specifications, the name Qualcomm is likely to have caught your eye. As a global semiconductor powerhouse, Qualcomm plays a pivotal role in the technology landscape. Renowned for its Snapdragon System on a Chip (SoC), Qualcomm dominates the mid- and high-end Android smartphone markets, boasting a substantial market share. Beyond smartphones, Qualcomm is a key player in developing 5G modems, contributing significantly to innovations like satellite-to-phone connectivity. This comprehensive overview delves into the essence of Qualcomm, shedding light on its history, pivotal contributions, and the technologies that define its prominence.
What is Qualcomm?
Qualcomm is an American company specializing in the design of semiconductors and wireless communications technologies. Notably, its Snapdragon SoC line powers a significant majority of Android smartphones, with estimates reaching up to 65% in specific segments, according to a recent Counterpoint report. Unlike hardware manufacturers, Qualcomm’s revenue is substantially derived from licensing its proprietary technologies. While it collaborates with third-party chipmakers like TSMC, Samsung Foundry, and GlobalFoundries for manufacturing, the end products, including SoCs and Snapdragon modems, are sold to smartphone giants such as Samsung, Xiaomi, and Oppo.
A Brief History of Qualcomm
Founded in 1985 in San Diego, Qualcomm began its journey as a contract research and development company. Initially focused on military and defense communications projects, Qualcomm achieved a significant breakthrough in 1988 with Omnitracs—a satellite tracking system for trucking companies. The success of Omnitracs propelled Qualcomm into CDMA cellular technology research. The company played a pivotal role in shaping the early US cellular industry, with most operators adopting Qualcomm’s CDMA standards for 2G networks. This influence extended globally, with Qualcomm assisting operators in various international markets in integrating CDMA technology.
Over the past decade, Qualcomm expanded its portfolio to include patents related to 4G LTE and 5G cellular technologies. Additionally, it ventured into developing its semiconductor designs based on the Arm architecture family in 2006. The introduction of the Snapdragon SoC in 2007 marked a significant milestone, being the first mobile SoC to operate at a clock speed of 1 GHz. Qualcomm’s commitment to innovation continued with acquisitions like Nuvia in 2021, enhancing its presence in the computing industry.
Qualcomm’s Diverse Portfolio
1. Snapdragon SoCs
Qualcomm’s Snapdragon SoC portfolio is a linchpin in the Android smartphone market. The Snapdragon 8 series, including the latest Snapdragon 8 Gen 1 and Snapdragon 8 Plus Gen 1, powers flagship and high-end smartphones. Boasting advanced CPU designs and cutting-edge Adreno GPUs, these SoCs are the driving force behind devices like Samsung’s Galaxy S22 series and OnePlus 10T.
2. Mid-Range Offerings
The Snapdragon 7 Gen 1 and Snapdragon 778G cater to the mid-range smartphone market. Devices such as Nothing Phone 1, Xiaomi 12 Lite, and Samsung Galaxy A73 5G leverage the capabilities of these mid-range SoCs.
3. Entry-Level and Budget Chips
In the budget and entry-level segment, Qualcomm introduces the Snapdragon 6 Gen 1 and Snapdragon 4 Gen 1. Anticipated to feature prominently in sub-$500 smartphones in 2023 and beyond, these chips bring reliable performance to a broader market.
Qualcomm vs. Competitors
While Qualcomm’s Snapdragon SoCs claim a lion’s share in the Android smartphone market, it doesn’t automatically crown Qualcomm as the unequivocal champion. Competitors like MediaTek, Samsung, and notably Apple, each present formidable alternatives. MediaTek, in particular, vies with Qualcomm across high-end, mid-range, and entry-level offerings. The rivalry often results in a performance seesaw, with real-world differences being marginal. Apple’s unique position in manufacturing its own chips grants it a significant edge, yet Qualcomm’s dominance in the Android realm remains unchallenged.
Future Outlook: Beyond Smartphones
Qualcomm’s influence extends far beyond smartphones, hinting at a future steeped in cutting-edge technologies. From augmented reality (AR) and artificial intelligence (AI) to Wi-Fi 7, Qualcomm is at the forefront of innovation. The Snapdragon XR2, powering Meta’s Quest 2 and Quest Pro headsets, exemplifies Qualcomm’s foray into AR/VR. Additionally, dedicated Tensor Accelerator chips in its latest SoCs emphasize Qualcomm’s commitment to AI and machine learning. In the computing arena, the Arm-based Snapdragon 8cx line for ultraportable laptops is emblematic of Qualcomm’s expansive vision.
Conclusion
In essence, Qualcomm stands as a technological linchpin, shaping the landscape of semiconductors and wireless communications. From its humble beginnings in military communications to its current dominance in the Android smartphone market, Qualcomm’s journey is marked by innovation and adaptability. As it ventures into emerging technologies, Qualcomm’s impact is poised to transcend conventional boundaries. Whether you’re a smartphone user benefiting from Snapdragon technology or an enthusiast eyeing the future of AR, Qualcomm’s influence is omnipresent, cementing its status as a stalwart in the realm of chip manufacturing.